【ベストコレクション】 p(x=x) probability distribution formula 217230-P(x=x) probability distribution formula
These facts are mentioned on the Basic Probability page and the Breif Summary of the Binomial Distribution page The lowest possible probability an outcome might have is 0 P(x=7)=0, the probability of getting 7 heads, when only 4 coins are flipped, is 0The normal distribution or Gaussian distribution is a continuous probability distribution that follows the function of where μ is the mean and σ 2 is the variance Note that standard deviation is typically denoted as σ Also, in the special case where μ = 0 and σ = 1, the distribution is referred to as a standard normal distributionIn order to do this, we define a function P, such that P(X = x) is the probability of the variable X having a value of x We could also ask for P(X < x), or P(X > x), for intervals instead of discrete values This will become even more relevant soon P is the variable's density function, and it characterizes that variable's distribution
Excel Probability Distributions
P(x=x) probability distribution formula
P(x=x) probability distribution formula-P(X = x) 50 38 25 13 0 Cumulative Distribution Function X = # of Heads in 3 tosses 0 1 2 3 C u mulative Probability P(XThe computational formula of the expected value and variance of a discrete probability distribution is, {eq}\mu=\sum(X_i\cdot P_i)\\ \sigma^2=\sum(X_i\mu)^2\cdot P(X_i)\\ {/eq} Answer and



Random Variables And Probability Distributions Make Me Analyst
Given random variables,, , that are defined on a probability space, the joint probability distribution for ,, is a probability distribution that gives the probability that each of ,, falls in any particular range or discrete set of values specified for that variable In the case of only two random variables, this is called a bivariate distribution, but the concept generalizes to anyConditional probability is the probability of one thing being true given that another thing is true, and is the key concept in Bayes' theorem This is distinct from joint probability, which is the probability that both things are true without knowing that one of them must be true For example, one joint probability is "the probability that your left and right socks are both black," whereas aC Find the 90 th percentile For each problem or part of a problem, draw a new graph Draw the xaxisShade the area that corresponds to the 90 th percentile Let k = the 90 th percentile The variable k is located on the xaxisP(x < k) is the area to the left of kThe 90 th percentile k separates the exam scores into those that are the same or lower than k and those that are the same or
We consider the standard normal distribution as an example Let X be random variable, x be a value of the random variable, and p be a probability Then A probability such as Pr(XX and y, P(X ≥xyX ≥x)=P(X ≥y) Proof The conditional probability is P(X ≥xyX ≥x) = P(X ≥xy,X ≥x) P(X ≥x) = P(X ≥xy) P(X ≥x) = e−λ(xy) e−λx = e−λy = P(X ≥y), which proves the memoryless property The memoryless property also has a geometric interpretation Consider the probability density(03) (07) 2 = 0441 1!/(31)!
E Probability Mass Function = A probability distribution involving only discrete values of X Graphically, this is illustrated by a graph in which the x axis has the different possible values of X, the Y axis has the different possible values of P(x) Properties 0 ≤ P(X = x) ≤ 1 Σ P(X = x) = 1 Probability distributions Page 2Let X be Binomial(n, p) The probability of having x "yes" events (also called "successes" in n trials is (where x!Probability Formula Probability formulas are useful for calculating the probability of an event to occur Probability is the branch of Mathematics that deals with numerical descriptions of the chances of an event to occur The probability of an event always lies between 0 and 1, where, 0 indicates an impossible event and 1 indicates a certain event


Parameters Of Discrete Random Variables


4 1 Probability Density Functions Pdfs And Cumulative Distribution Functions Cdfs For Continuous Random Variables Statistics Libretexts
The concept of probability distribution formula is very important as it basically estimates the expected outcome on the basis of all the possible outcomes for a given range of data One of the most important parts of a probability distribution is the definition of the function as every other parameter just revolves around it ProbabilitySelect the method or formula of your choice For a number p in the closed interval 0,1, the inverse cumulative distribution function (ICDF) of a random variable X determines, where possible, a value x such that the probability of X ≤ x is greater than or equal to pBecause the probability that the player makes the shot is p = 07, then the probability of failure will be the complement q = 1 − p = 03 We can calculate this probability longhand, by multiplying the probabilities of the three independent events P(X = 3) = P(failure)×P(failure)×P(success) = 03 × 03 × 07 = 0063



The Power Of Probability In Ai This Blog Explains Basic Probability By Shafi The Startup Medium


The Uniform Distribution Introduction To Statistics
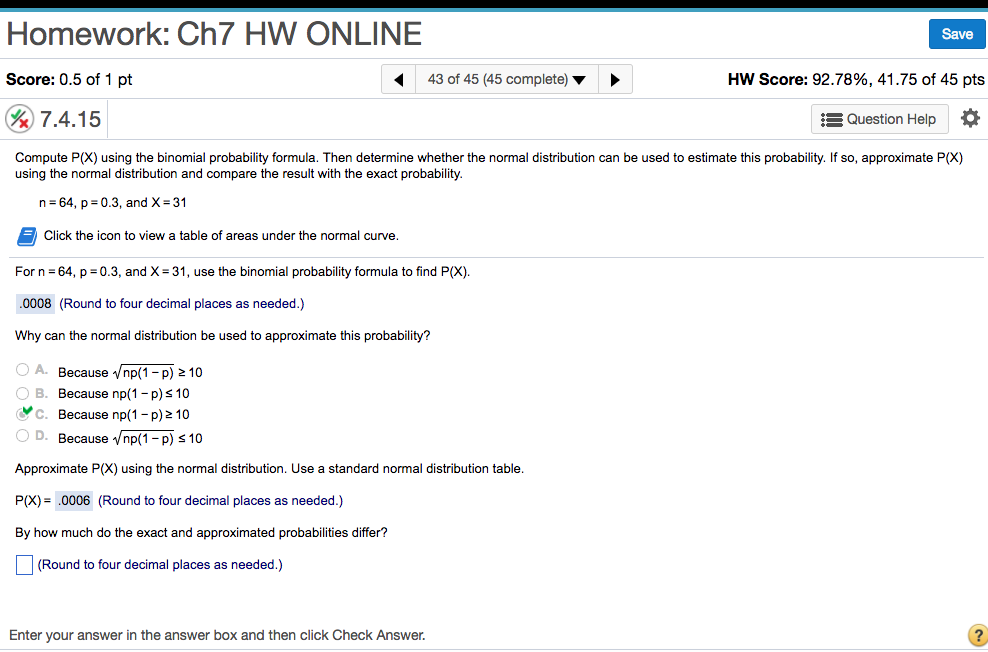
P(c < x < d) is the same as P(c ≤ x ≤ d) because probability is equal to area We will find the area that represents probability by using geometry, formulas, technology, or probability tables In general, integral calculus is needed to find the area under the curve for many probability density functionsCompute P(x) using the binomial probability formula Then determine whether the normal distribution can be used to estimate this probability If so, approximate P(x) using the normal distribution and compare the result with the exact probability n=78, p=077, and x = 56 For n=78, p=077, and x = 56, find P(x) using the binomial probability distributionSimilarly, Probability of selecting 2 damage lights = P(G) X P(D) X P(D) X 3 (multiplied by 3 because the good light can be selected in 3 ways, ie, either in 1 st round or 2 nd or 3 rd round) So,


Excel Probability Distributions


Binomial Formula Explained
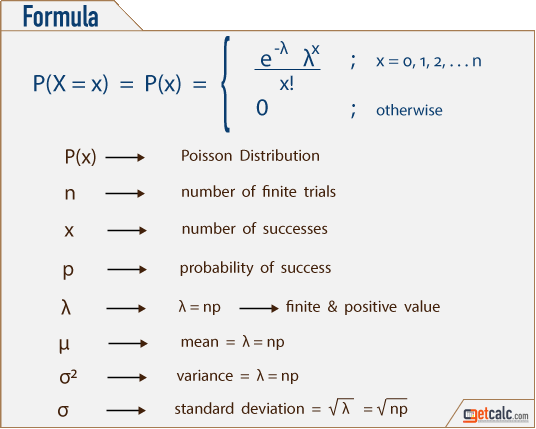
The probability density function (PDF) of a random variable, X, allows you to calculate the probability of an event, as follows For continuous distributions, the probability that X has values in an interval (a, b) is precisely the area under its PDF in the interval (a, b) For discrete distributions, the probability that X has values in an interval (a, b) is exactly the sum of the PDF (also called the probability mass function) of the possible discrete values of X in (a, b)The Binomial Probability distribution of exactly x successes from n number of trials is given by the below formula P (X) = nCx px qn – x Where, n = Total number of trials x = Total number of successful trials p = probability of success in a single trial q = probability of failure in a single trial = 1pThe Poisson Distribution Calculator will construct a complete poisson distribution, and identify the mean and standard deviation A poisson probability is the chance of an event occurring in a given time interval


Http People Math Harvard Edu Knill Teaching Math464 1997 Math464 565 1997 Pdf


3
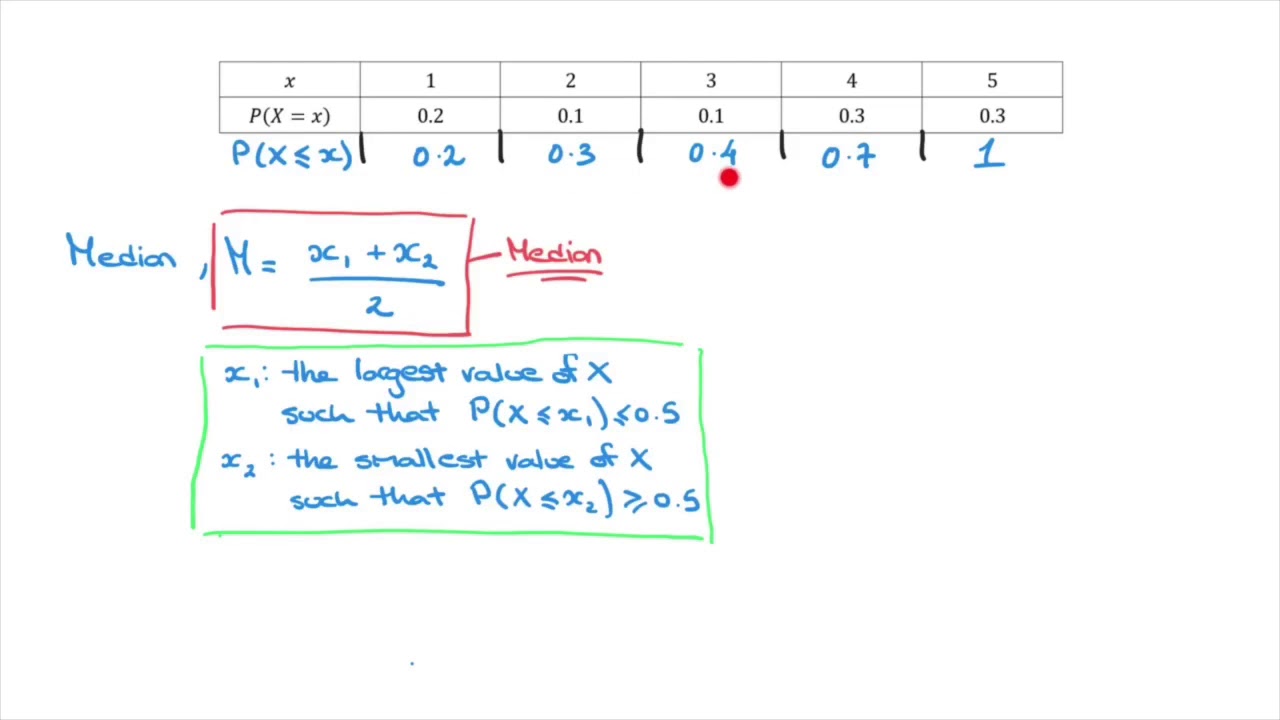
F X (x) = P r (X=x) = P ({s ∈ S X(s) = x}) Probability Distribution Table The table could be created based on the random variable and possible outcomes Say, a random variable X is a realvalued function whose domain is the sample space of a random experiment The probability distribution P(X) of a random variable X is the system of numbersIn this case, we'll look for the value of P(X ≤ x) and subtract from one Examples 1 What is the probability that 5 is greater than x in a normally distributed data given that the mean is 6, and the standard deviation is 07 Solution P(X < 5) the first step is to find the z score We find that using the formula above z = (x – μ (meanThe probability distribution is described by the cumulative distribution function F(x), which is the probability of random variable X to get value smaller than or equal to x F(x) = P(X ≤ x) Continuous distribution The cumulative distribution function F(x) is calculated by integration of the probability density function f(u) of continuous


Poisson Distribution Calculator Formula Examples
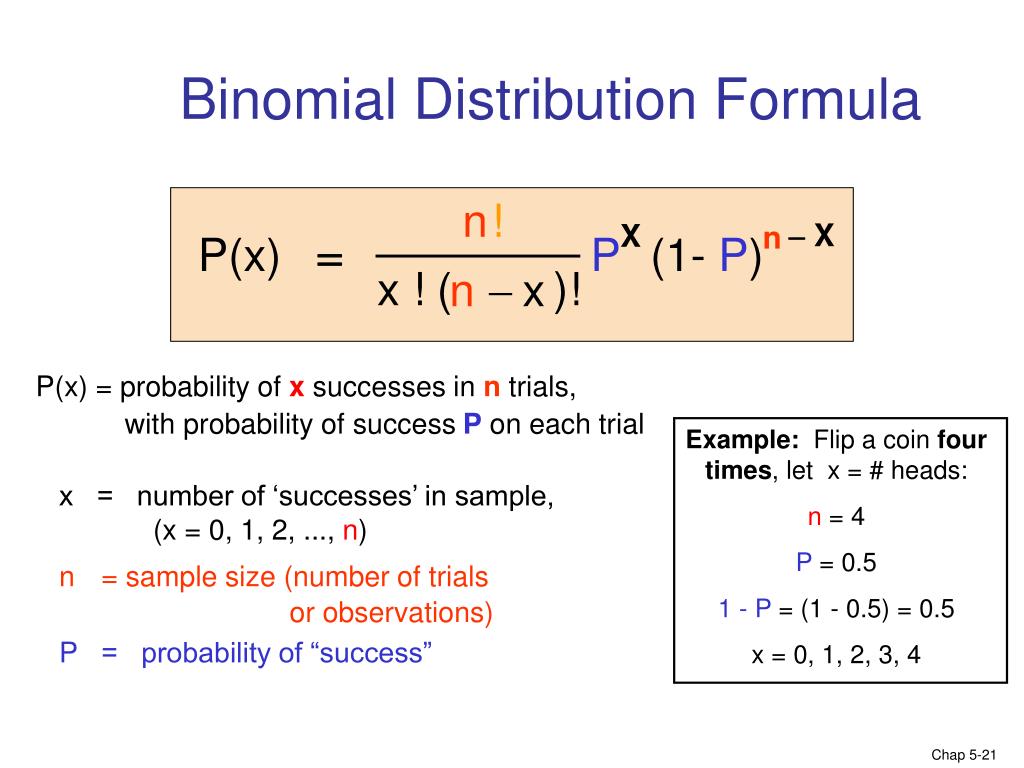


Ppt Chapter 5 Discrete Random Variables And Probability Distributions Powerpoint Presentation Id
Face is proportional to the square of the number obtained on its face Obtain the probability distribution table associated with this experiment Solution Since P(x) ∝ x => P(x) = kx 2 where k is the proportionality constant and x are the numbers from 1 to 6 Also from the two conditions listed above we know that the sum of all probabilities is 1P (X < 1) = P (X = 0) P (X = 1) = 025 050 = 075 Like a probability distribution, a cumulative probability distribution can be represented by a table or an equation In the table below, the cumulative probability refers to the probability than the random variable X is less than or equal to x Number of headsThe concept of probability distribution formula is very important as it basically estimates the expected outcome on the basis of all the possible outcomes for a given range of data One of the most important parts of a probability distribution is the definition of the function as every other parameter just revolves around it Probability



Constructing A Probability Distribution For Random Variable Video Khan Academy
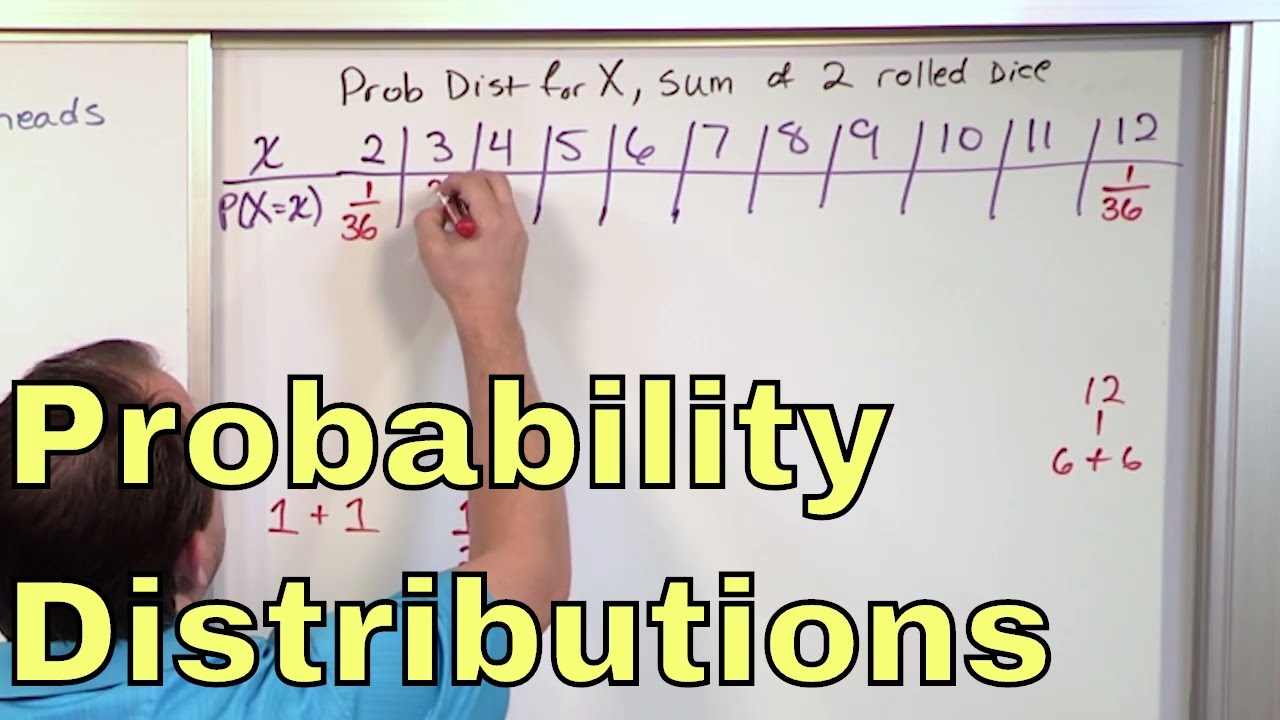


02 Random Variables And Discrete Probability Distributions Youtube
We have made a probability distribution for the random variable X And the random variable X can only take on these discrete values It can't take on the value half or the value pi or anything like that So this, what we've just done here is constructed a discrete probability distribution Let me write that downPx q nx where x!(nx)!Probability Density Function of Normal Distribution, Standard Normal Distribution Formula PDF of Normal Distribution = P(x) = (1/(σsqrt(2π)))e (xm) 2 / (2σ 2 )



Calculate The Mean For The Following Discrete Probability Distribution H 3 0 3 P X 6 0 04 9 Homeworklib
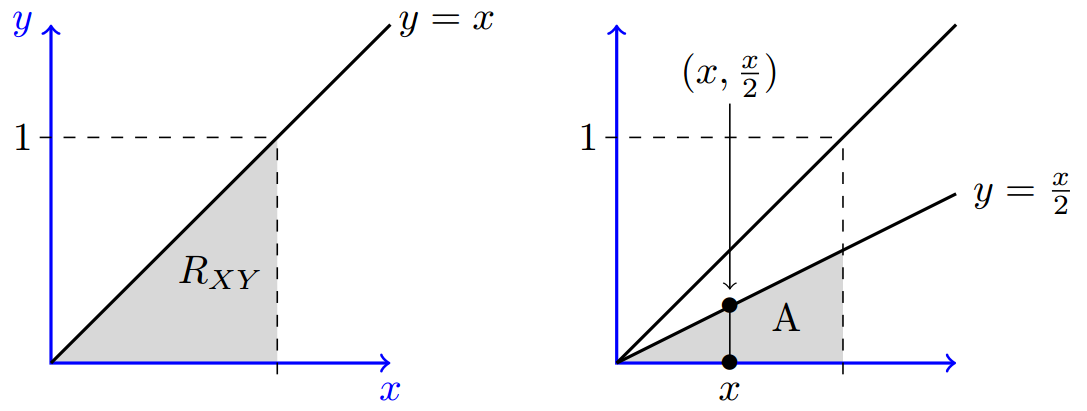


Joint Probability Density Function Joint Continuity Pdf
So, the probability P(x) for a random experiment or discrete random variable x, is distributed asP(0) = ¼P(1) = ½P(2) = 1/4P(x) = ¼ ½ ¼ = 1 What is the probability distribution used for?The probability of success is given by the geometric distribution formula P ( X = x) = p × q x − 1 Where − p = 30 % = 03 x = 5 = the number of failures before a success Therefore, the required probability P ( X = 5) = 03 × ( 1 − 03) 5 − 1, = 03 × ( 07) 4, ≈ 0072 ≈ 72 % Previous Page Print PageC Find the 90 th percentile For each problem or part of a problem, draw a new graph Draw the xaxisShade the area that corresponds to the 90 th percentile Let k = the 90 th percentile The variable k is located on the xaxisP(x < k) is the area to the left of kThe 90 th percentile k separates the exam scores into those that are the same or lower than k and those that are the same or
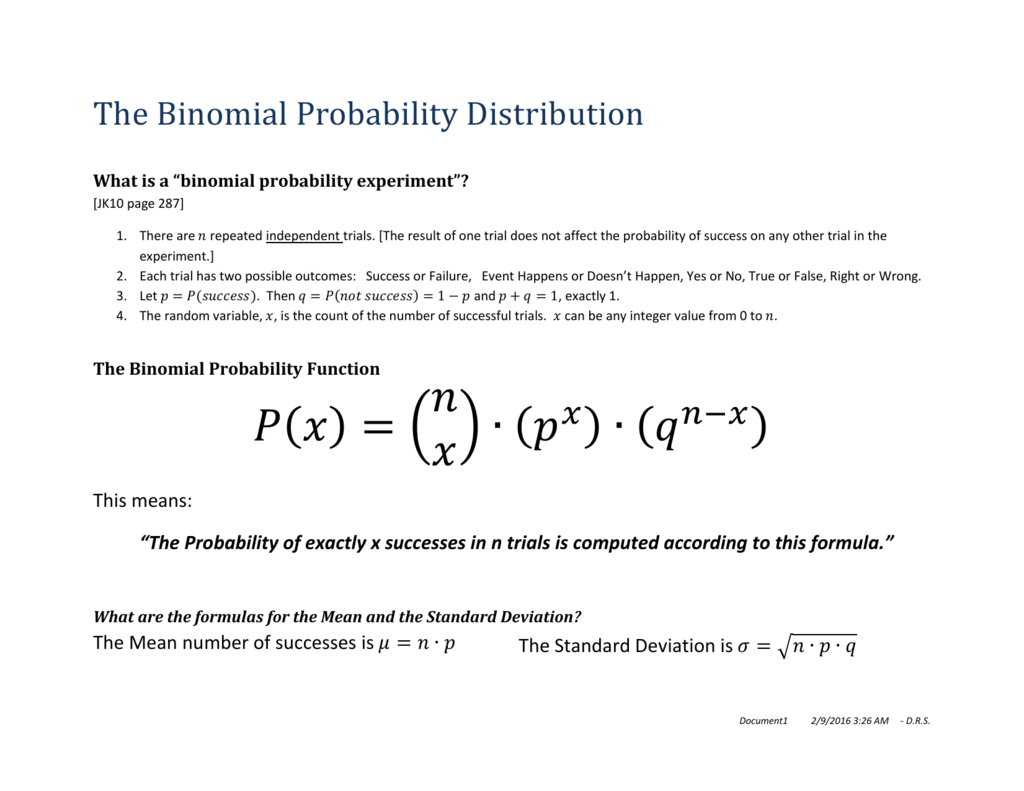


What Is A Binomial Probability Experiment



Probability And Random Variable Powerpoint Slides
C Poisson distributions where µ= npThe probability distribution is one of the important concepts in statisticsThe computational formula of the expected value and variance of a discrete probability distribution is, {eq}\mu=\sum(X_i\cdot P_i)\\ \sigma^2=\sum(X_i\mu)^2\cdot P(X_i)\\ {/eq} Answer and



Choosing The Probability Distributions Dr Ganapathi Pulipaka Facebook



Content Mean And Variance Of A Continuous Random Variable
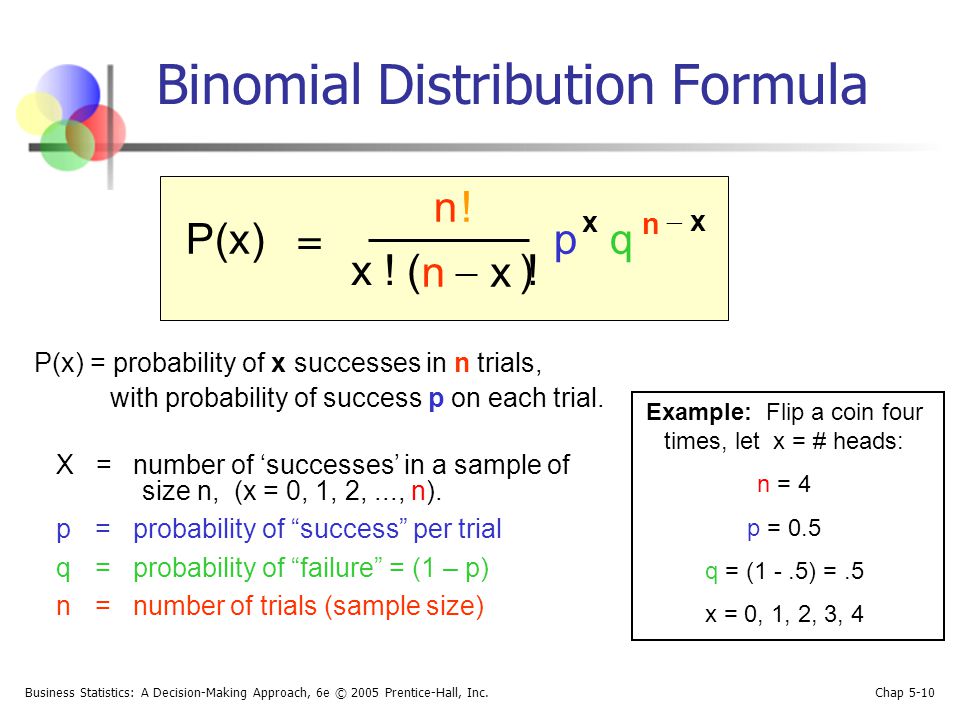
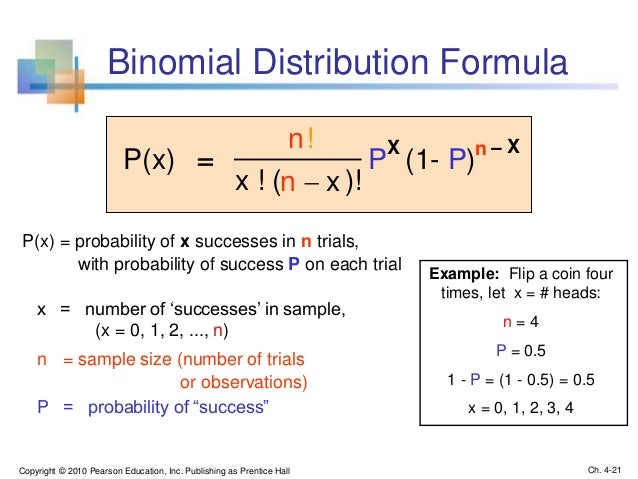
Binomial Distribution – Formula First formula b(x,n,p)= nCx*P x* (1P) nx for x=0,1,2,n where – b is the binomial probability x is the total number of successes p is chances of a success on an individual experiment n is the number of trials n>0 ∴ p,q≥0 ∑b(x,n,p) = b(1) b(2) b(n) = 1Compute P(x) using the binomial probability formula Then determine whether the normal distribution can be used to estimate this probability If so, approximate P(x) using the normal distribution and compare the result with the exact probability n=78, p=077, and x = 56 For n=78, p=077, and x = 56, find P(x) using the binomial probability distributionTI84 Computing the binomial formula, \(P(X = {x)={n\choose x}p^x(1p)^{nx}}\) Use 2ND VARS, binompdf to evaluate the probability of exactly \(x\) occurrences out of \(n\) independent trials of an event with probability \(p\text{}\) Select 2ND VARS (ie DISTR) Choose Abinompdf (use the down arrow to scroll down) Let trials be \(n\text



Solved Consider The Random Variable X With Probability Di Chegg Com



Pareto Distribution Wikipedia
= 1) Check in Example 1 n=3 , p=03 P(X=1) = 3!It can be calculated using the formula for the binomial probability distribution function (PDF), aka probability mass function (PMF) f(x), as follows where X is a random variable, x is a particular outcome, n and p are the number of trials and the probability of an event (success) on each trial The term (n over x) is read "n choose x" andA random variable X is said to be a Bernoulli random variable with parameter p, shown as X ∼ B e r n o u l l i ( p), if its PMF is given by P X ( x) = { p for x = 1 1 − p for x = 0 0 otherwise where 0 < p < 1 Figure 32 shows the PMF of a B e r n o u l l i ( p) random variable



Random Variable And Its Probability Distribution Ma Economics Karachi University



Probability And Random Processes Kings College Of Engineering
X n x n − px (1p) nx Binomial Probability Distribution FormulaProbability of x successes in n trials of a binomial experiment In Section 42 of the Larson text, we see that the probability of a certain number of successes, x, out of n trials in a binomial experiment is given as Formula P(x) = nCx (p)x (q)nx To calculate P(x) you need to know two things 1Stack Exchange network consists of 176 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack Exchange



Expectation Variance Of A Discrete Random Variable Ppt Download
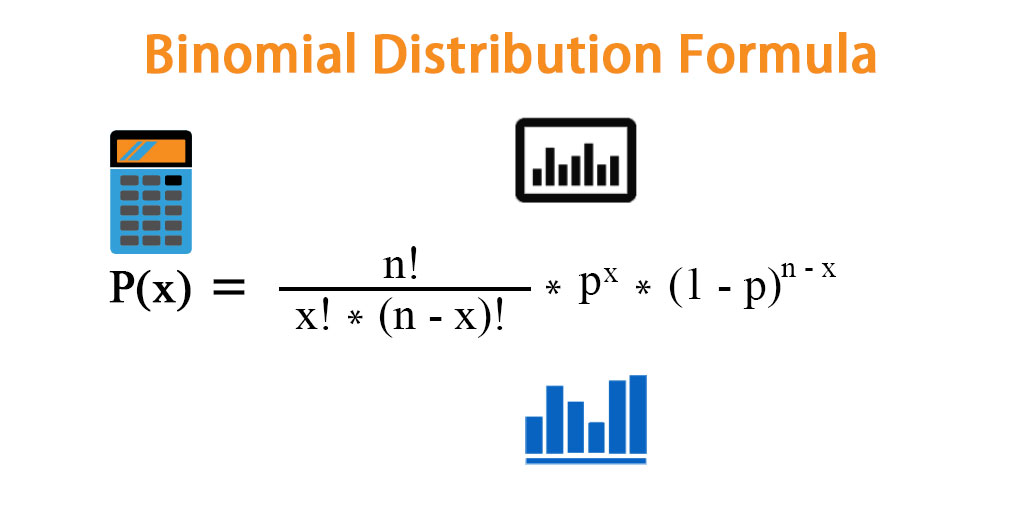


Binomial Distribution Formula Calculator Excel Template
The probability distribution of a discrete random variable X is a listing of each possible value x taken by X along with the probability P (x) that X takes that value in one trial of the experiment The mean μ of a discrete random variable X is a number that indicates the average value of X over numerous trials of the experimentThe weight of each bottle (Y) and the volume of laundry detergent it contains (X) are measured Marginal probability distribution If more than one random variable is defined in a random experiment, it is important to distinguish between the joint probability distribution of X and Y and the probability distribution of each variable individuallyProbability distribution of continuous random variable is called as Probability Density function or PDF Given the probability function P(x) for a random variable X, the probability that X belongs to A, where A is some interval is calculated by integrating p(x) over the set A ie



Some Special Discrete Probability Distributions Pdf Free Download



If In A Table All Possible Values Of A Random Variable Are Given Their Corresponding Probabilities Then This Table Is Called As
The normal distribution or Gaussian distribution is a continuous probability distribution that follows the function of where μ is the mean and σ 2 is the variance Note that standard deviation is typically denoted as σ Also, in the special case where μ = 0 and σ = 1, the distribution is referred to as a standard normal distribution= x(x1)(x2)1, and 0!A Probability distributions 1 P(x) = x • P(x) is calculated for each value of x 2 Mean of a probability distribution µ = E(x) = 1 x • P(x) 3 Variance of a probability distribution V(x) = 1x2 • P(x) E(x)2 B Binomial distributions P(x) = n!


Www Coconino Edu Resources Files Pdfs Academics Sabbatical Reports Kate Kozak Chapter 5 Pdf



Example 34 Find Mean Of Binomial Distribution B 4 1 3
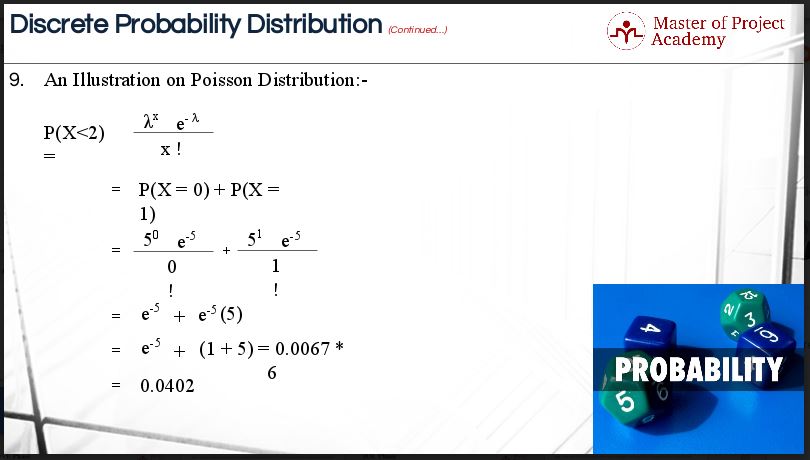


How To Calculate Probability Using The Poisson Distribution



Discrete Random Variable An Overview Sciencedirect Topics


Http Homepage Divms Uiowa Edu Rdecook Stat Notes Ch4 Pt3 Pdf



Random Variables And Probability Distributions Make Me Analyst
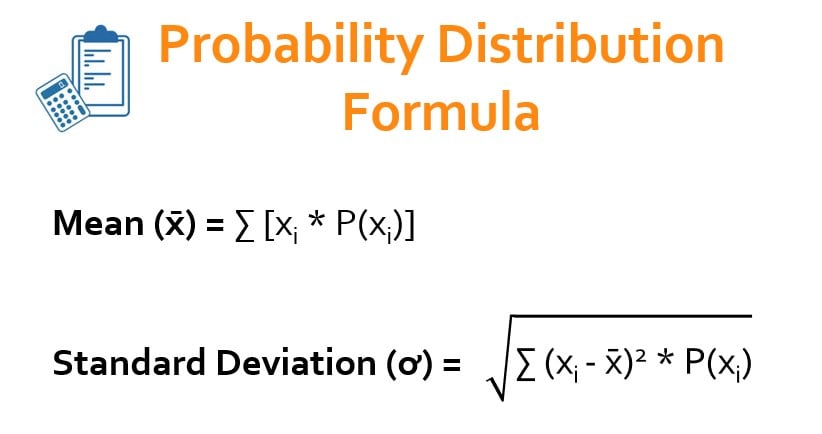


Probability Distribution Formula Examples With Excel Template



Binomial Distribution Calculator



Parameters Of Discrete Random Variables



Tutorial Probability Distributions In Python Datacamp



Content Probability Functions
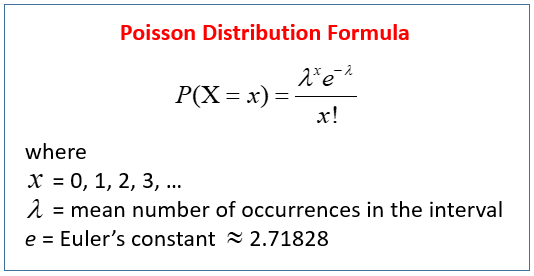


Poisson Distribution Video Lessons Examples And Solutions


Binomial Formula Explained
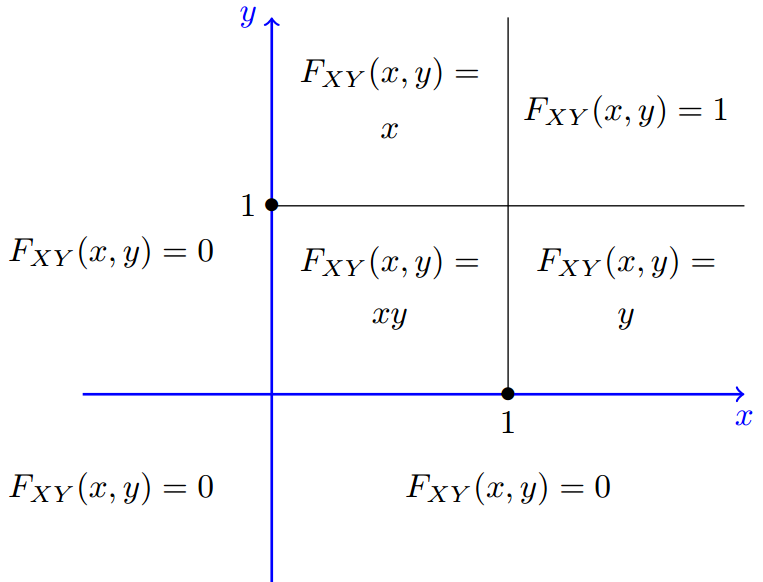


Joint Cumulative Distribution Function Examples Cdf



Probability And Random Processes Kings College Of Engineering


Random Variables And Probability Distributions Make Me Analyst


2


Probability Density Function



Chapter 5 Discrete Probability Distributions 1 Slideshow And Powerpoint Viewer 2 Random Variables Tila College Is A Small Private School With 2 500 Students According To The Registrar S Off


The Binomial Distribution



Lmdsnznhxqe Tm


Chapter 5 Discrete And Continuous Probability Distributions Ppt Download
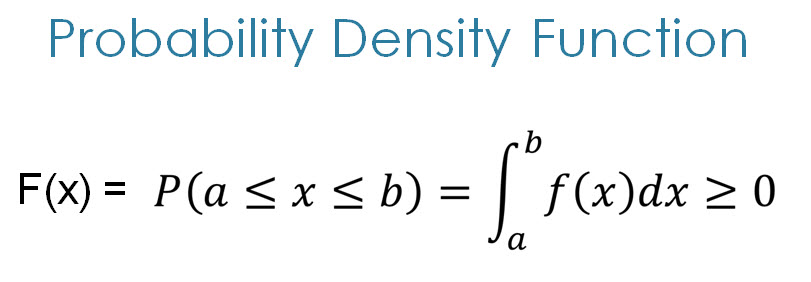


Continuous Probability Distributions Env710 Statistics Review Website


Q Tbn And9gcrlhqgb0nmkf9opqbiv2phzg Ohrc0phczwr2pmbzcj0huiq0yh Usqp Cau



Random Variable And Its Probability Distribution Ma Economics Karachi University


Chap04 Discrete Random Variables And Probability Distribution



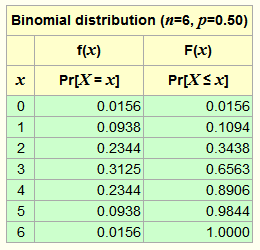
1 3 6 6 18 Binomial Distribution



How To Compute The Probabilities Of Discrete Distribution Mathematics Stack Exchange



Section6 3


Www Stat Auckland Ac Nz Fewster 210 Notes 16s2 Ch4annotated Pdf



Binomial Distribution Real Statistics Using Excel
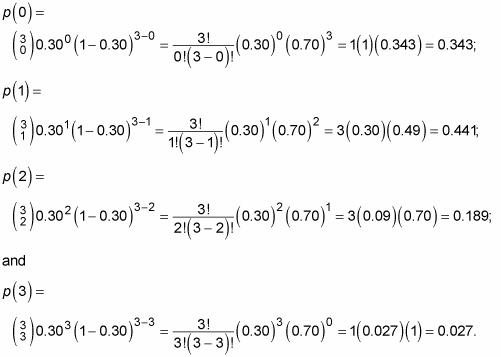


How To Find Binomial Probabilities Using A Statistical Formula Dummies


Solved Compute P X Using The Binomial Probability Formul Chegg Com


4 2 Discrete Random Variables Probability Mass Functions An Introduction To Probability And Simulation



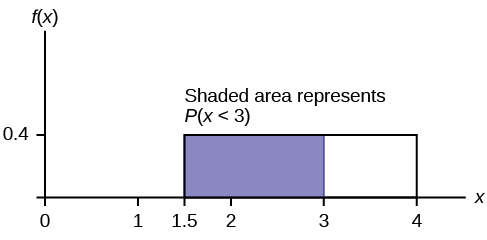
Continuous Probability Functions Introduction To Statistics


1 Probability Distributions Ghci Grade 12 Mathematics Of Data Management



Random Variable And Its Probability Distribution Properties And Examples



Understanding Probability Distributions Statistics By Jim


3



Determine The Value Of K For A Random Variable Distribution Ib Sl Test Youtube


Www Colorado Edu Amath Sites Default Files Attached Files Ch4 Pdf



Probability And Random Variable Powerpoint Slides


Binomial Distribution Calculator



Formula For The Mean Of The Probability Distribution Docx Computing The Mean Of A Discrete Probability Distribution Lesson 3 Formula For The Mean Of Course Hero
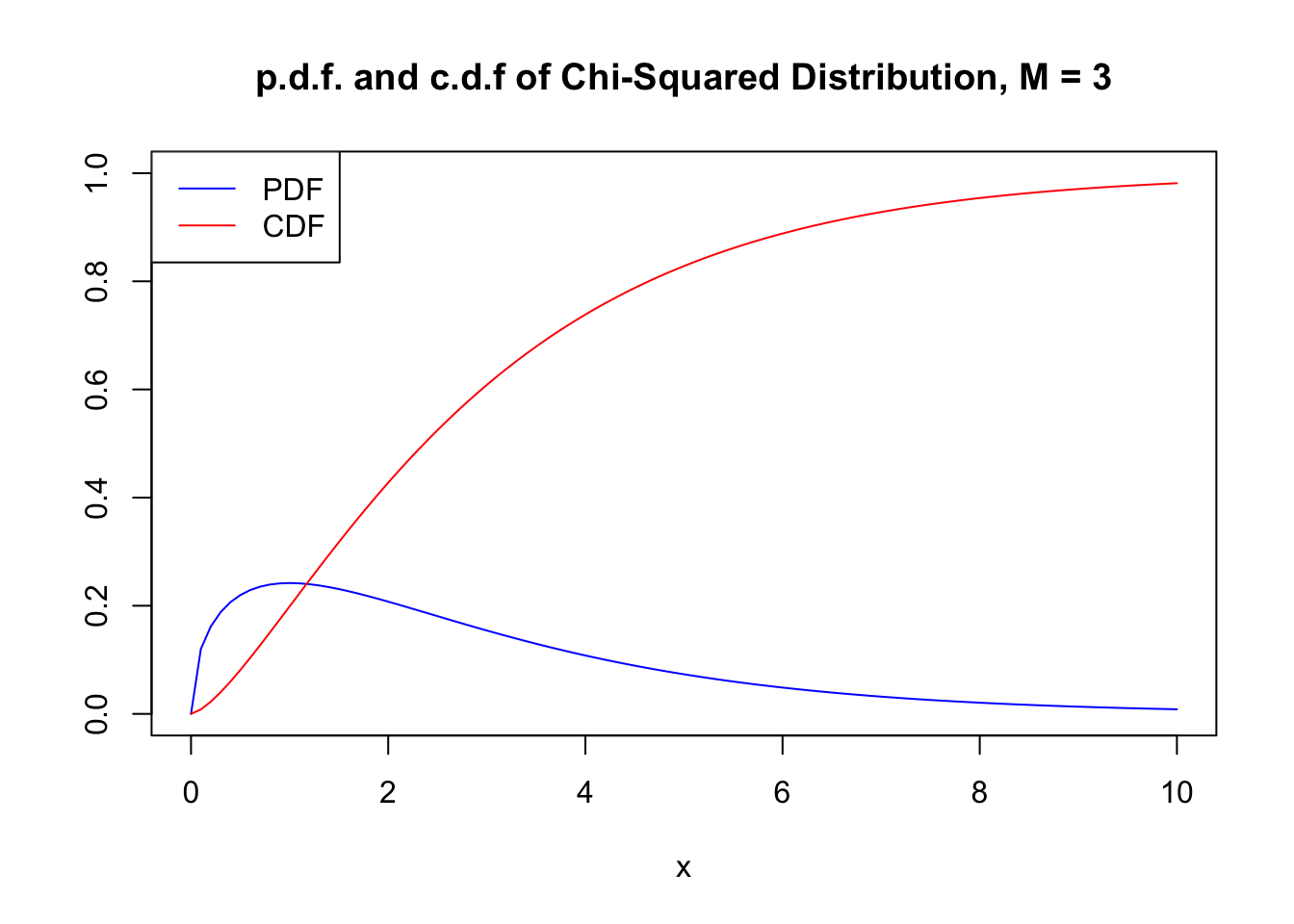


2 1 Random Variables And Probability Distributions Introduction To Econometrics With R



Using Probability Distributions In R Dnorm Pnorm Qnorm And Rnorm Data Science Blog Understand Implement Succed


5 4 The Exponential Distribution Statistics Libretexts
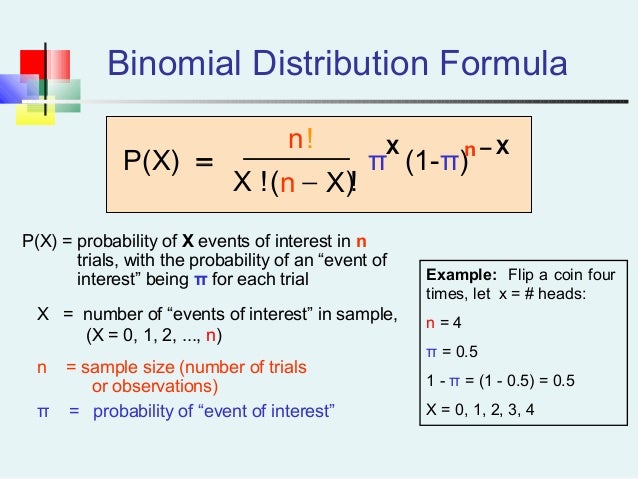


Probability Distribution 2
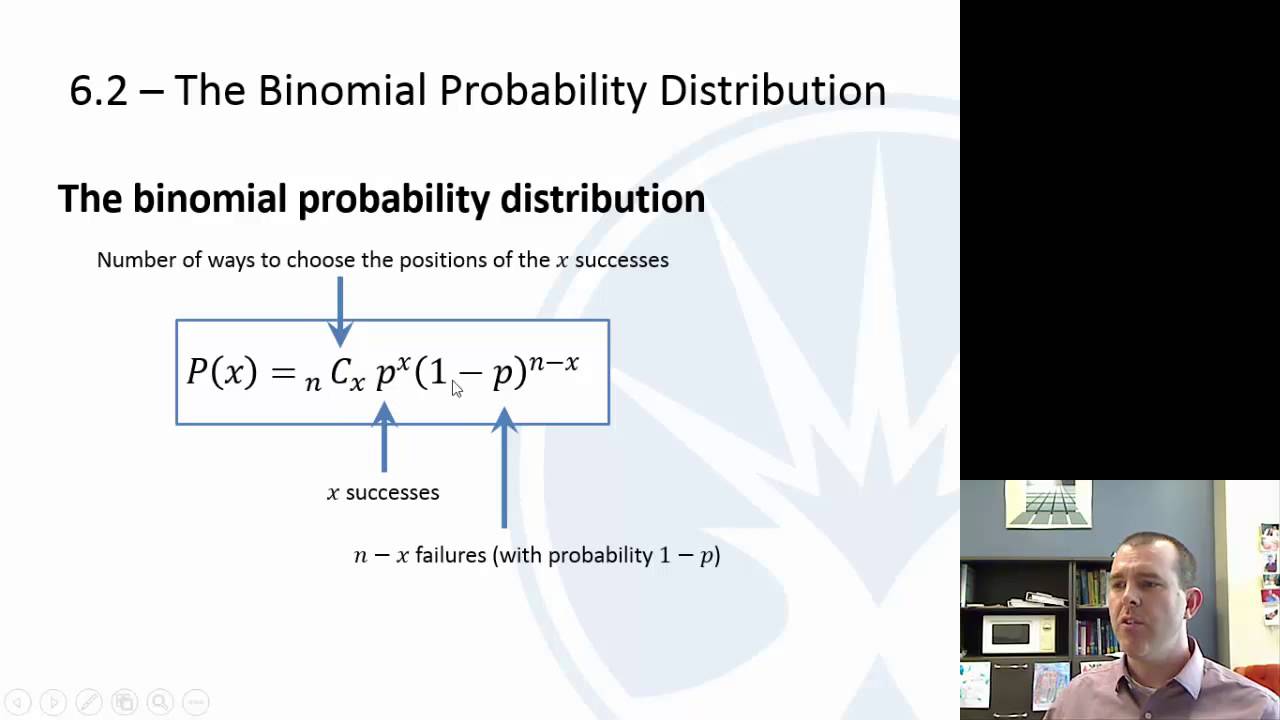


Chapter 6



Probability And Random Variable Powerpoint Slides
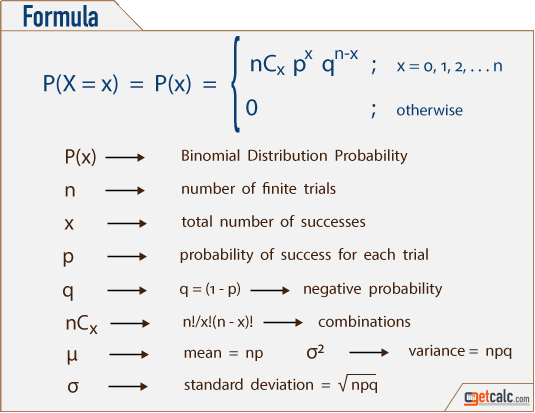


Binomial Distribution Formulas Calculator
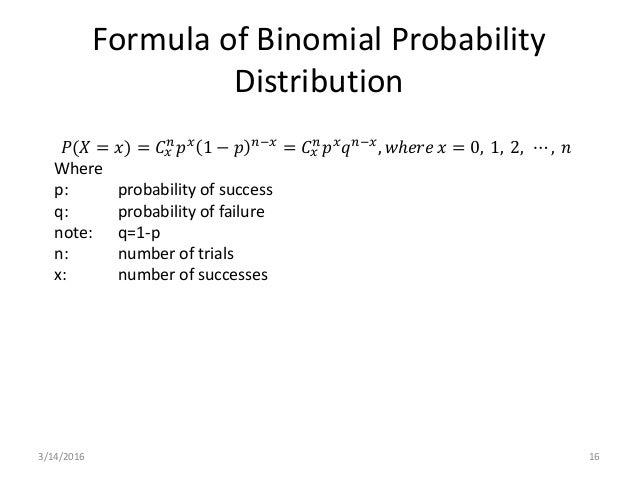


Binomial Distribution


Faculty Math Illinois Edu Hildebr 370 408discrete1 Pdf



Ta Notes Week7 Bao Zhigang Tutorial Notes Of Math2421 Week Brief Summary Of Studocu
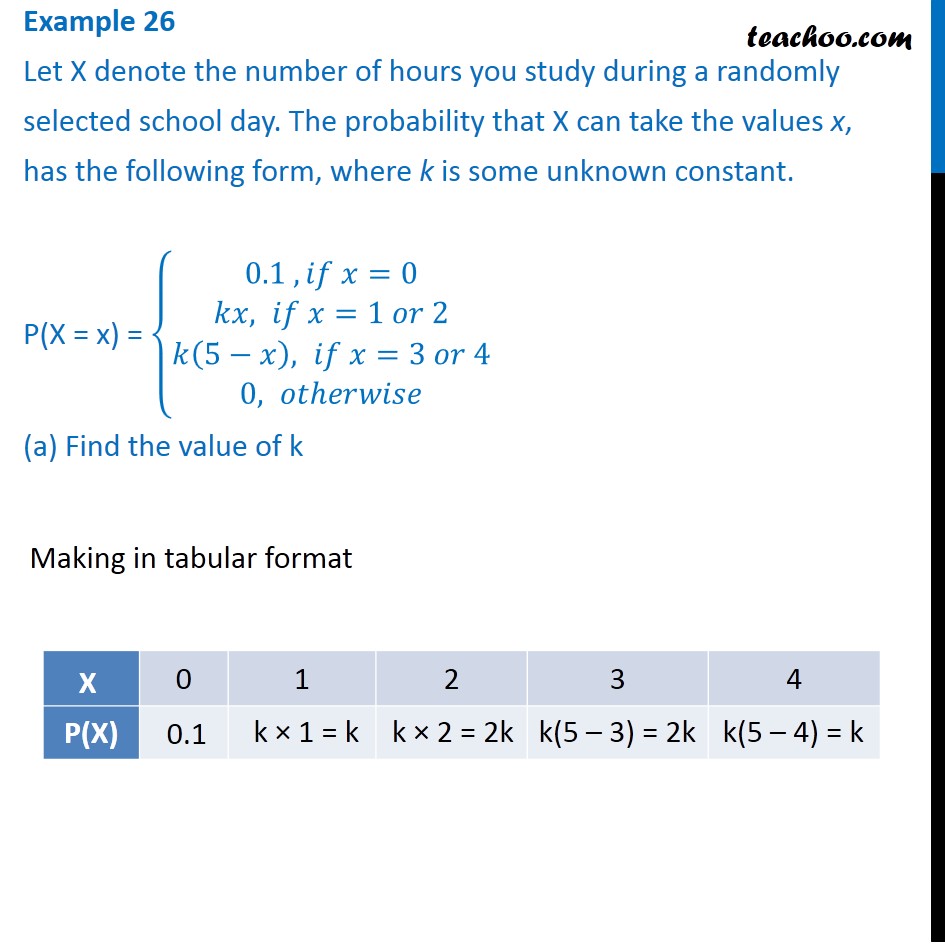


Example 26 Let X Denote The Number Of Hours You Study During A Randoml


Probability Density Function


Probability Distributions For Discrete Random Variables


11 Probability Distributions Concepts


Aswarphysics Weebly Com Uploads 4 6 2 1 Advanced Level Mathematics Mechanics 1 Part4 Pdf



Probability With Discrete Random Variable Example Video Khan Academy


Http Faculty Elac Edu Deutschl Doc Math 227 Class notes Chapter 5 Pdf



Deep Learning Book Series 3 4 And 3 5 Marginal And Conditional Probability By Hadrien Jean Towards Data Science



Maths For Ml Probability Distributions By Raghunath D Medium
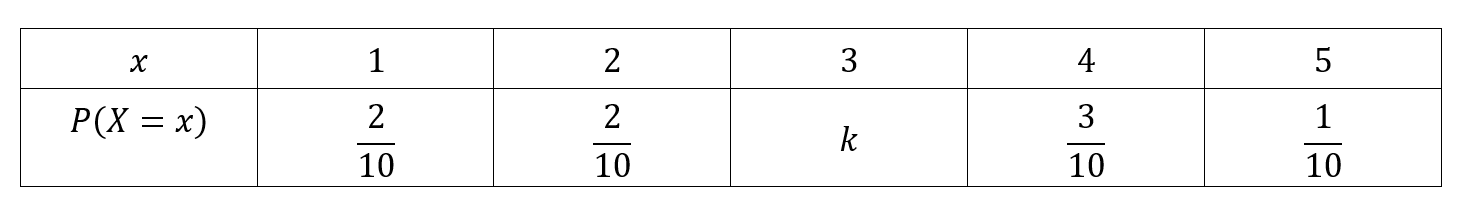


Parameters Of Discrete Random Variables


Binomial Random Variables Biostatistics College Of Public Health And Health Professions University Of Florida
/invest-chart17-01-b6840b5dae61481aa99e8d0c7907de34.png)


Using Common Stock Probability Distribution Methods



The Binomial Distribution S Cool The Revision Website


Random Variables
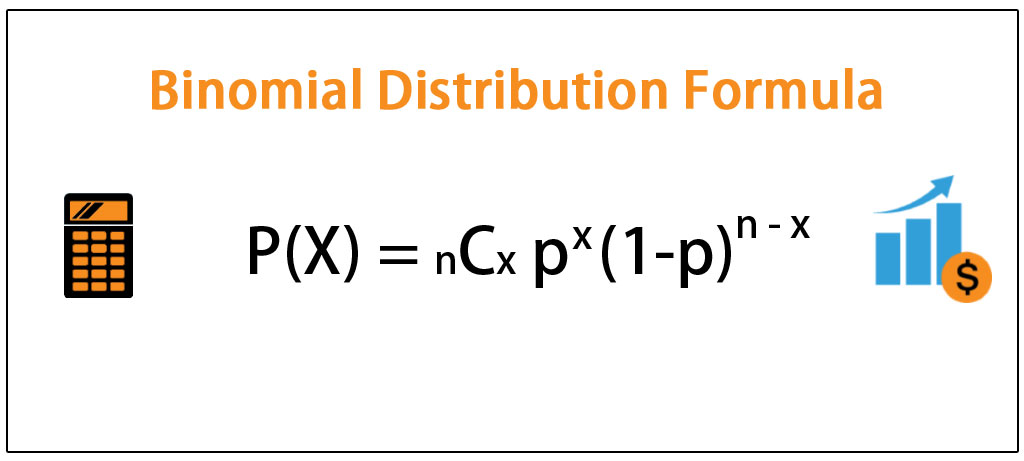


Binomial Distribution Formula Step By Step Calculation Example


Www Stat Auckland Ac Nz Fewster 210 Notes 16s2 Ch4annotated Pdf



Class Practice On Discrete Probability Distributions 3



Probability Mass Function Wikipedia


Excel Probability Distributions
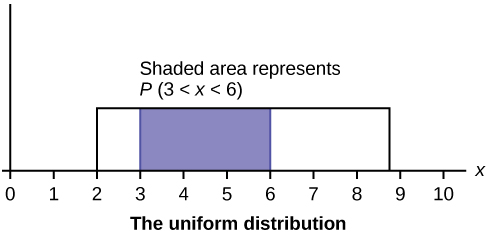


Properties Of Continuous Probability Density Functions Introductory Business Statistics



Random Variables And Probability Distributions Pdf Free Download



What Is Poisson Distribution Kdnuggets



Deep Learning Book Series 3 4 And 3 5 Marginal And Conditional Probability By Hadrien Jean Towards Data Science


コメント
コメントを投稿